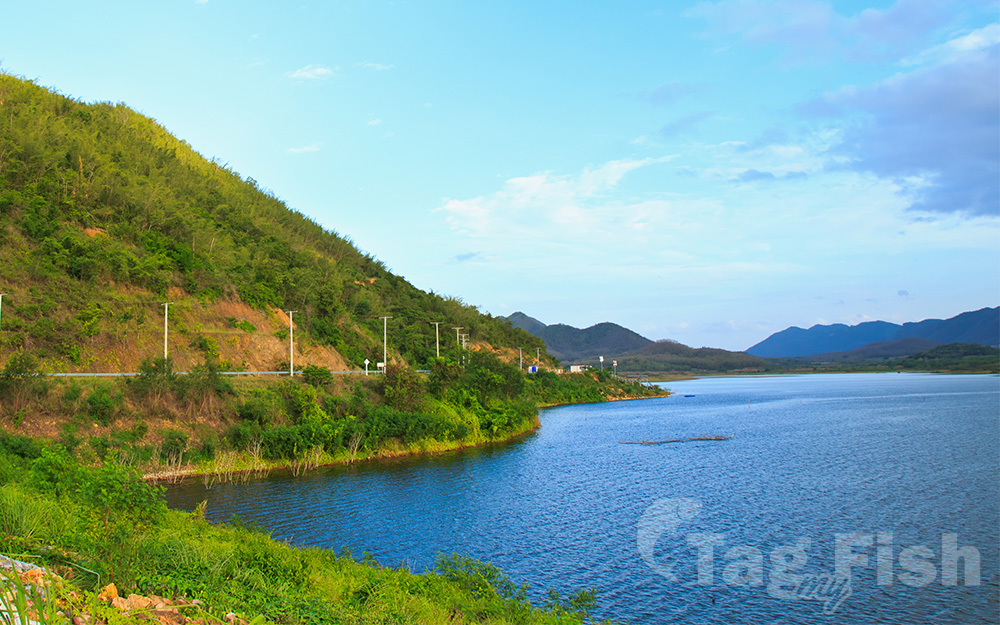
Quabbin Reservoir

Water type: Artificial lake
Basin: Swift River (Ware River tributary) -> Ware River -> Chicopee River -> Connecticut River -> Atlantic Ocean -> Planet Earth
Continent:
North America
Climate:
Continental
Country:
United States of America (USA)
Perciformes - Perches
Salmoniformes - Salmons and Trouts
Esociformes - Pikes
Siluriformes - Catfishes
Centrarchiformes - Basses and sunfishes
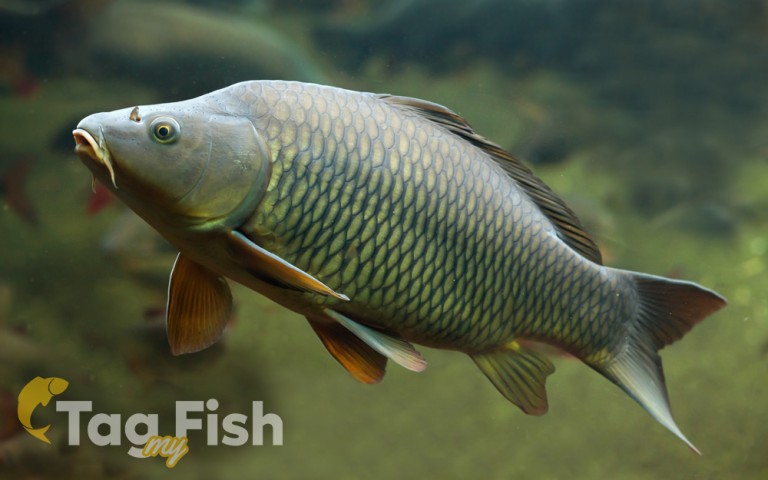
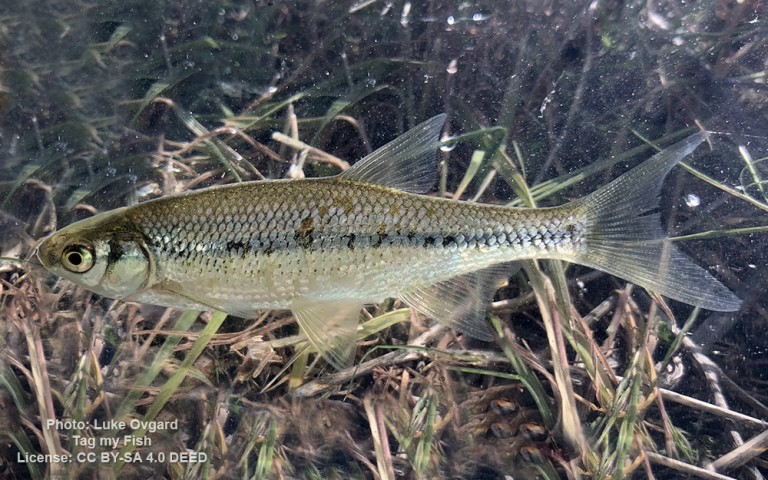
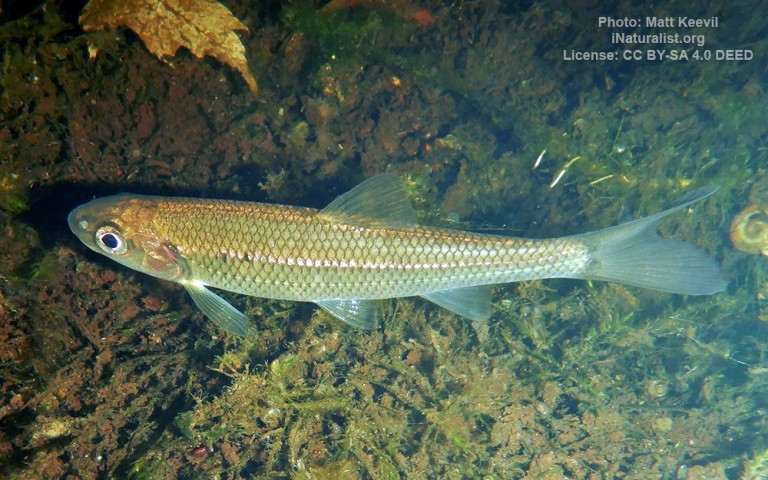
Cypriniformes - Carps
Acipenseriformes - Sturgeons and Paddlefish
Moroniformes - Temperate basses
Clupeiformes - Herrings
Pleuronectiformes - Flatfishes
Percopsiformes - Trout-perches
Cyprinodontiformes - Toothcarps
Petromyzontiformes - Lampreys
Perciformes - Perches
Salmoniformes - Salmons and Trouts
Esociformes - Pikes
Siluriformes - Catfishes
Centrarchiformes - Basses and sunfishes
Cypriniformes - Carps
Acipenseriformes - Sturgeons and Paddlefish
Moroniformes - Temperate basses
Clupeiformes - Herrings
Pleuronectiformes - Flatfishes
Percopsiformes - Trout-perches
Cyprinodontiformes - Toothcarps
Petromyzontiformes - Lampreys
The Quabbin Reservoir is the largest inland body of water in Massachusetts, United States, and was built between 1930 and 1939. Along with the Wachusett Reservoir, it is the primary water supply for Boston, 65 miles (105 km) to the east, and 40 other cities and towns in Greater Boston. The Quabbin also supplies water to three towns west of the reservoir and acts as backup supply for three others. By 1989, it supplied water for 2.5 million people, about 40% of the state’s population at the time. It has an aggregate capacity of 412 billion US gallons (1,560 GL) and an area of 38.6 square miles (99.9 km2).