Your catch,
online.
Share your catch with the world! Learn from fellow anglers and level up your fishing skills! Explore new fishing spots!
REGISTER FOR FREE Join the ultimate community for anglers!Available on the App Store and Google Play
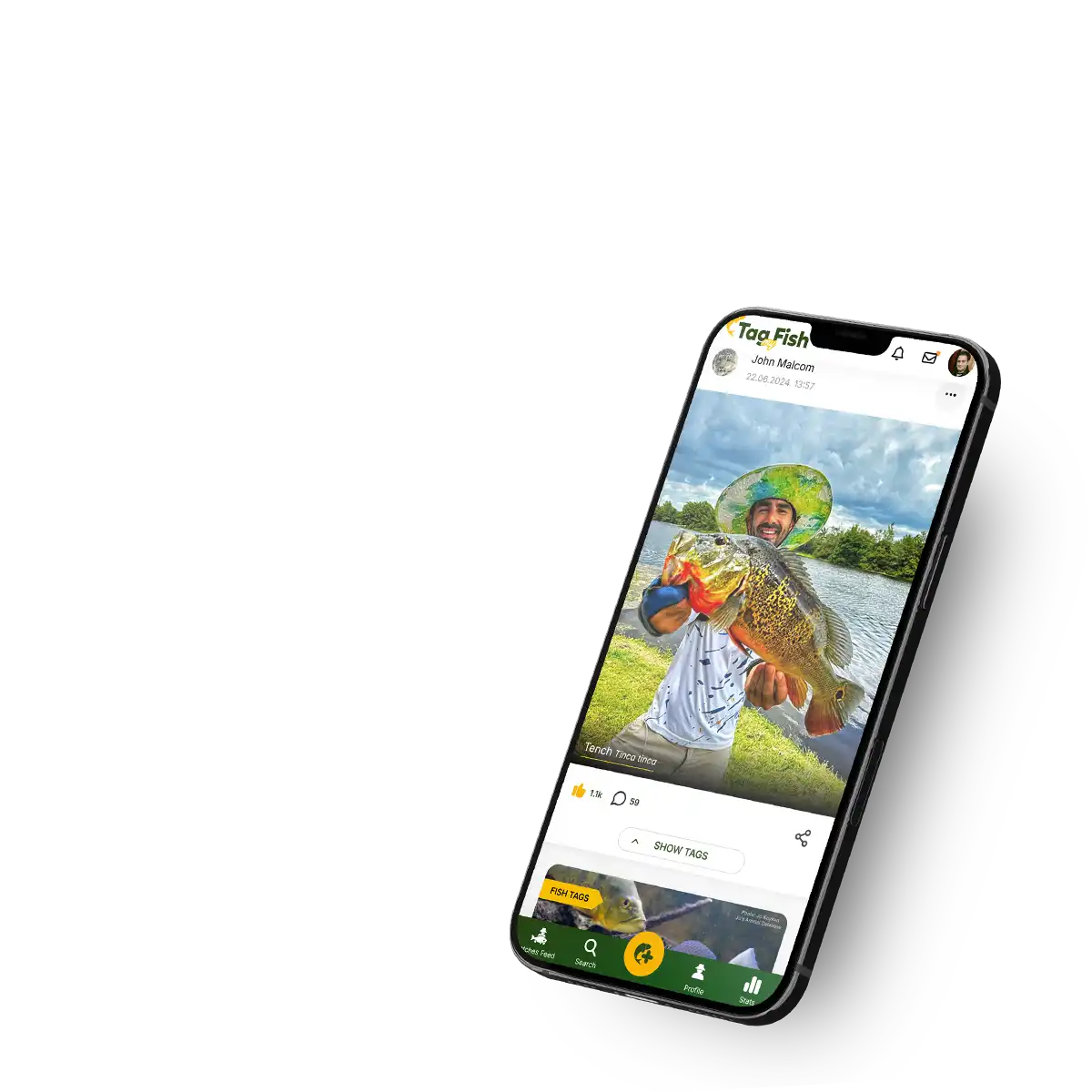

Catches (15693)
Join the Tag My Fish community and share your catch with the world!
Explore millions of catches from around the globe, discover top fishing spots, and learn the best tactics, baits, and lures. Tag your fishing gear to remember what helped you catch the fish of a lifetime!
Share your underwater discoveries with fellow divers and scientists!
Report ecological issues to help authorities take actions toward solutions!
Register now

Fishes of the World (35179)
Discover everything about fish species!
From the deepest oceans to the smallest mountain streams, our project is your ultimate guide to the world of fishes. Explore the latest taxonomy, with all species meticulously organized by genus, family, order, and class.
Explore fish species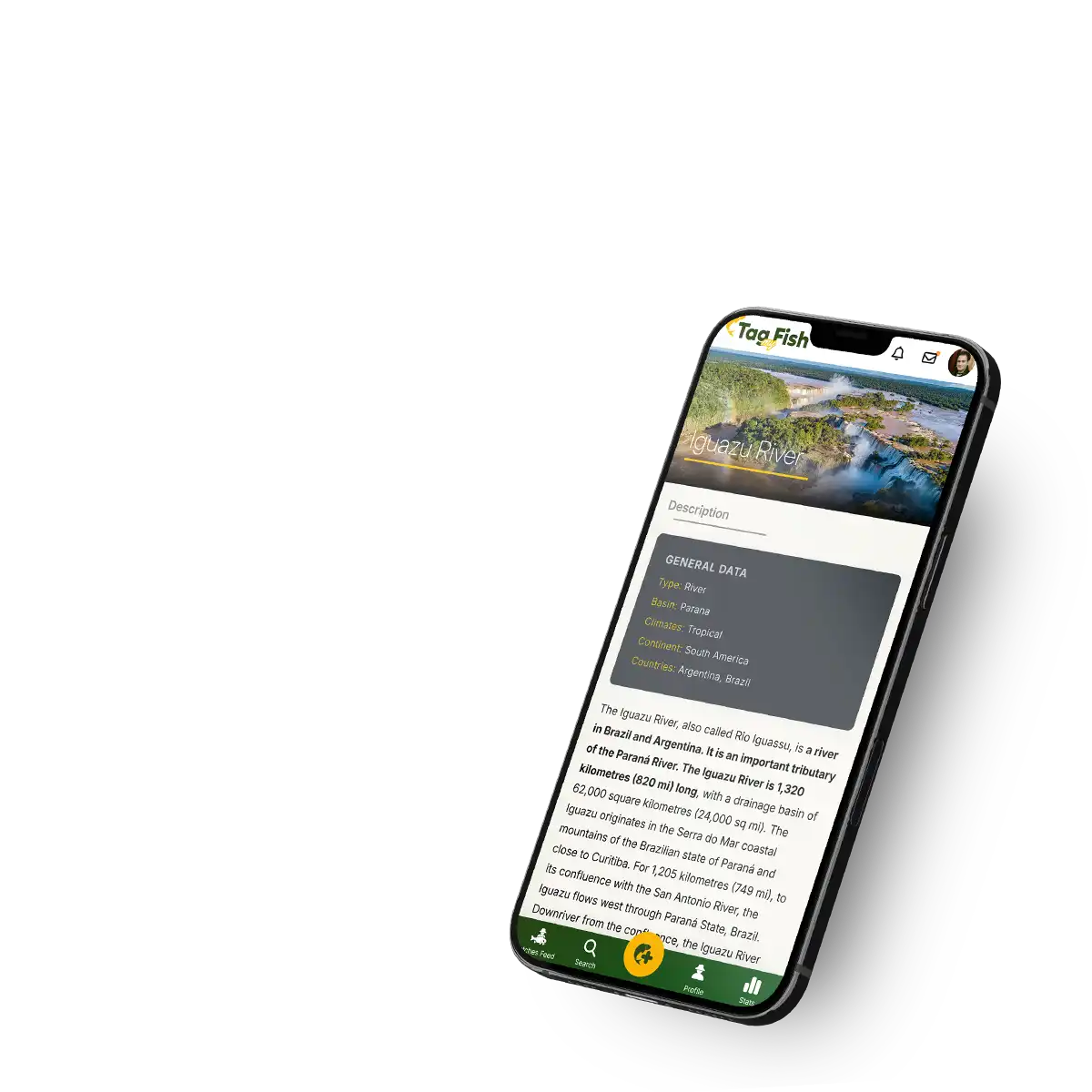

Water Atlas (11923)
Explore the one-of-a-kind Tag My Fish Water Atlas, a unique database connecting all waters in a seamless map.
Follow the journey of streams as they form creeks, creeks merging into rivers, and rivers creating deltas and estuaries, ultimately flowing into seas and oceans. Discover basic information about each waterbody, learn about the fish species you can expect, or browse through all tagged catches. Add your catch to the gallery of a waterbody and help others gain valuable information and improve their chances of a great catch!
Explore waters
 English
English
 Spanish
Spanish
 German
German
 French
French
 Serbian
Serbian
 Russian
Russian


 4.9
4.9