Clariidae - Airbreathing catfishes

Classification
Description
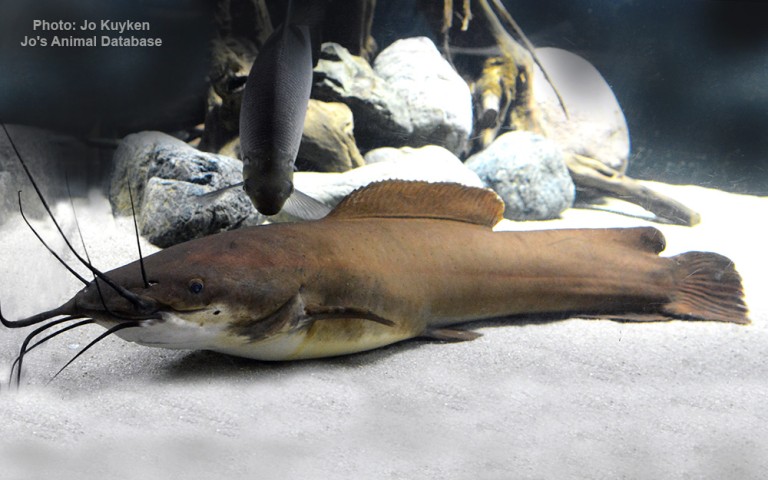
Airbreathing catfish comprise the family Clariidae of the order Siluriformes. Sixteen genera and about 116 species of clariid fishes are described; all are freshwater species. Other groups of catfish also breathe air, such as the Callichthyidae and Loricariidae.
Distribution
Although clariids occur in India, Syria, southern Turkey, and large parts of Southeast Asia, their diversity is the largest in Africa.
Description
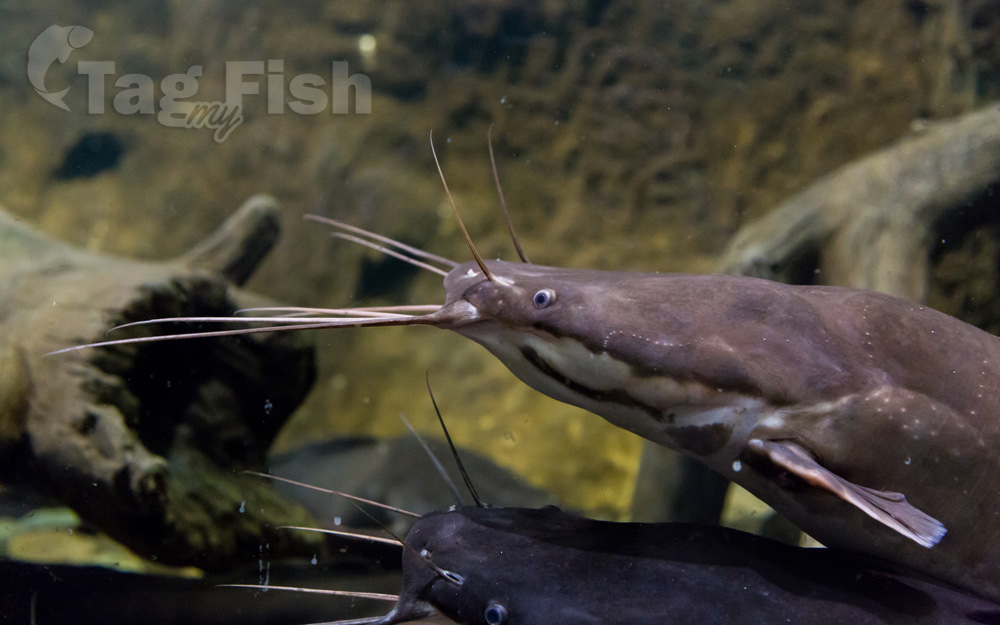
Clariid catfish are characterized by an elongated body, the presence of four barbels, long dorsal and anal fins, and especially by the autapomorphic presence of a suprabranchial organ, formed by tree-like structures from the second and fourth gill arches. This suprabranchial organ, or labyrinth organ, allows some species the capability of traveling short distances on land (walking catfish).
The dorsal fin base is very long and is not preceded by a fin spine. The dorsal fin may or may not be continuous with the caudal fin, which is rounded. Pectoral and pelvic fins are variously absent in some species. Some fish have small eyes and reduced or absent pectoral and pelvic fins for a burrowing lifestyle. A few species are blind.
Within the family Clariidae, body forms range from fusiform (torpedo-like) to anguilliform (eel-like). As species become more eel-shaped, a whole set of morphological changes has been observed, such as decrease and loss of the adipose fin, continuous unpaired fins, reduction of paired fins, reduction of the eyes, reduction of the skull bones, and hypertrophied jaw muscles.