Angelshark
(Squatina squatina)
Classification
General data
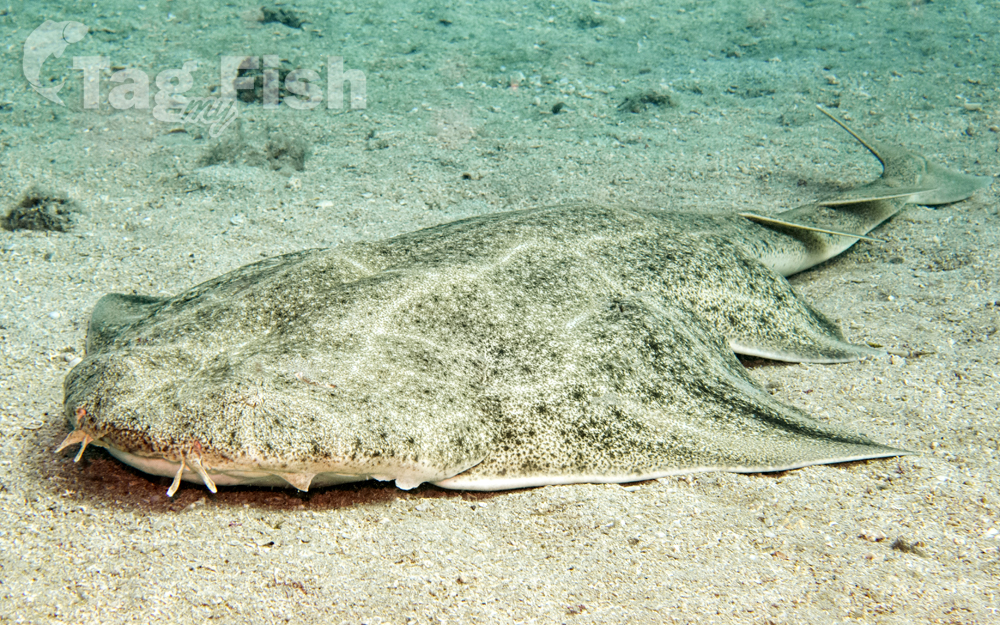
Squatina squatina, the angelshark or monkfish, is a species of shark in the family Squatinidae (known generally also as angel sharks), that were once widespread in the coastal waters of the northeastern Atlantic Ocean. Well-adapted for camouflaging itself on the sea floor, the angelshark has a flattened form with enlarged pectoral and pelvic fins, giving it a superficial resemblance to a ray. This species can be identified by its broad and stout body, conical barbels, thornless back (in larger individuals), and grayish or brownish dorsal coloration with a pattern of numerous small light and dark markings (that is more vivid in juveniles). It measures up to 2.4 m (7.9 ft) long.
Like other members of its family, the angelshark is a nocturnal ambush predator that buries itself in sediment and waits for passing prey, mostly benthic bony fishes, but also skates and invertebrates. An aplacental viviparous species, females bear litters of seven to 25 pups every other year. The angelshark normally poses little danger to humans, though if provoked, it is quick to bite. Since the mid-20th century, intense commercial fishing across the angelshark\'s range has decimated its population via bycatch – it is now locally extinct or nearly so across most of its northern range, and the prospects of the remaining fragmented subpopulations are made more precarious by its slow rate of reproduction. As a result, the International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed this species as Critically Endangered.
One of the largest members of its family, female angelsharks can attain a length of 2.4 m (7.9 ft) and males 1.8 m (5.9 ft); the maximum reported weight is 80 kg (180 lb).
This species shares in common with other angelsharks a flattened body and large, wing-like pectoral fins whose anterior lobes are not fused to the head. The head and body are very broad and stocky, with small eyes positioned dorsally and followed by a pair of larger spiracles. A pair of unadorned barbels occurs in front of the nares, as well as a smooth or weakly fringed flap. Folds of skin with a single triangular lobe are present on the sides of the head. The teeth are small, sharp, and of similar shape in both jaws.
The pectoral and pelvic fins are wide with rounded tips; the two dorsal fins are positioned on the muscular tail behind the pelvic fins. The anal fin is absent, and the caudal fin has a larger lower lobe than upper. The dermal denticles are small, narrow, and pointed, and cover the entire upper and most of the lower body surface. There are patches of small spines on the snout and over the eyes. Small individuals have a row of thorns down the middle of the back. The coloration is gray to reddish or greenish brown above, with many small black and white spots, and white below. Juveniles are more ornately patterned than adults, with pale lines and darker blotches. The dorsal fins have a darker leading margin and lighter trailing margin. Some individuals have a white spot on the back of the neck.
Distribution and habitat
The angelshark occurs in the temperate waters of the northeastern Atlantic, from southern Norway and Sweden to the Western Sahara and the Canary Islands, including around the British Isles and in the Mediterranean. According to the IUCN, it is possible that it has been extirpated from the North Sea. It remains extant around the Canary Islands, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, Israel, Turkey, northern Cyprus, eastern Greece (the Aegean Sea), the Adriatic Sea of eastern Italy, Sicily, Malta, Corsica, Ireland and western Britain. Its modern presence in parts of the Mediterranean is unknown, such as around Madeira, the Azores, Morocco, Egypt, continental Spain and France, Crete, Syria, Sardinia, western Greece and western Italy. This benthic shark inhabits the continental shelf, preferring soft substrates such as mud or sand, and can be found from near the coast to a depth of 150 m (490 ft). It sometimes enters brackish environments. Northern angelshark subpopulations migrate northward in summer and southward in winter.











