Humber estuary

Largest tributaries
Acipenseriformes - Sturgeons and Paddlefish
Syngnathiformes - Pipefishes and Seahorses
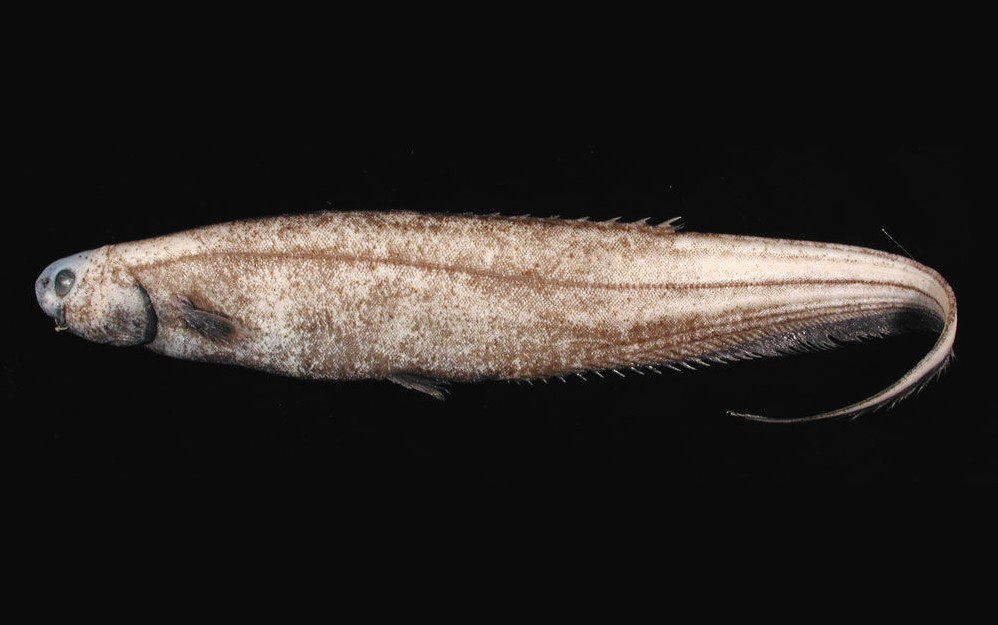
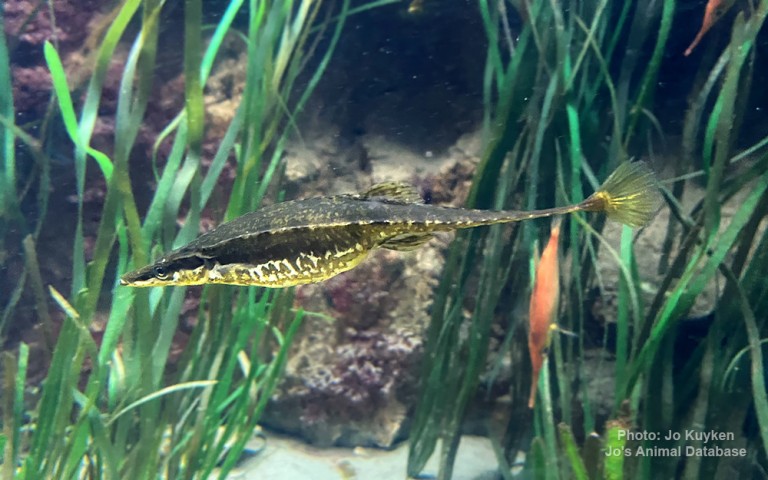
Anguilliformes - Eels and morays
Salmoniformes - Salmons and Trouts
Moroniformes - Temperate basses
Mugiliformes - Mullets
Clupeiformes - Herrings
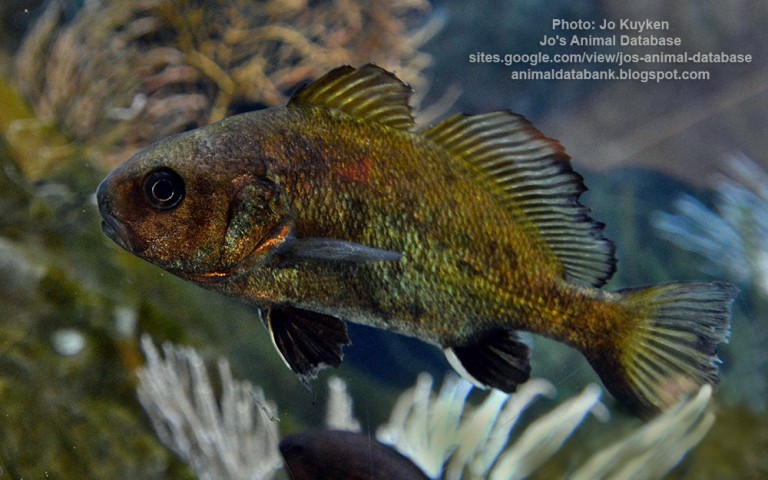
Perciformes - Perches
Spariformes - Breams and porgies
Beloniformes - Needlefishes
Labriformes - Wrasses
Scombriformes - Mackerels
Scorpaeniformes - Mail-cheeked fishes
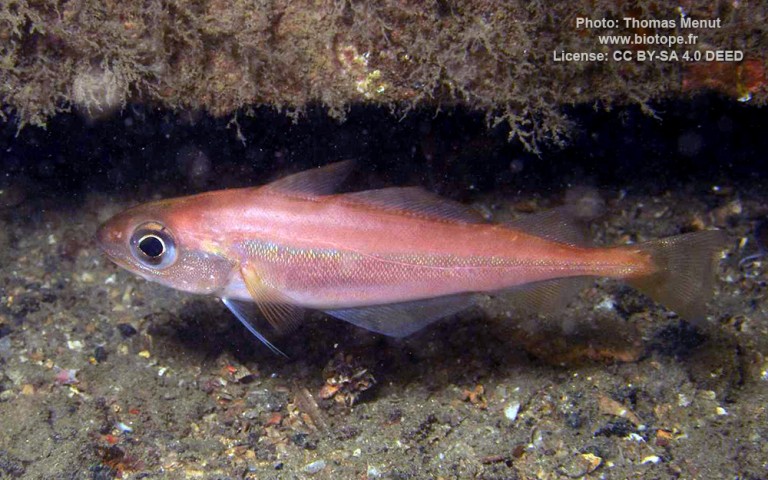
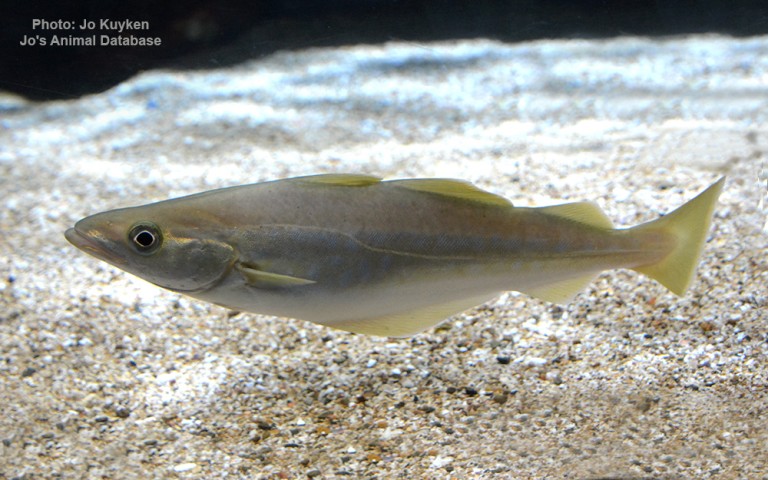
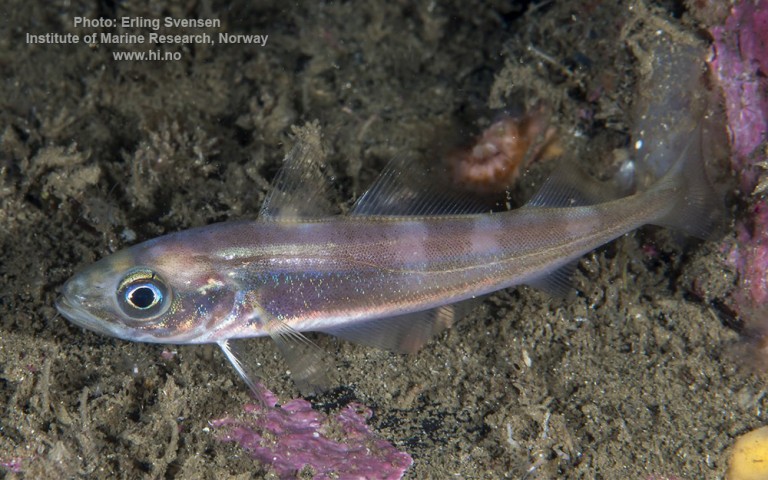
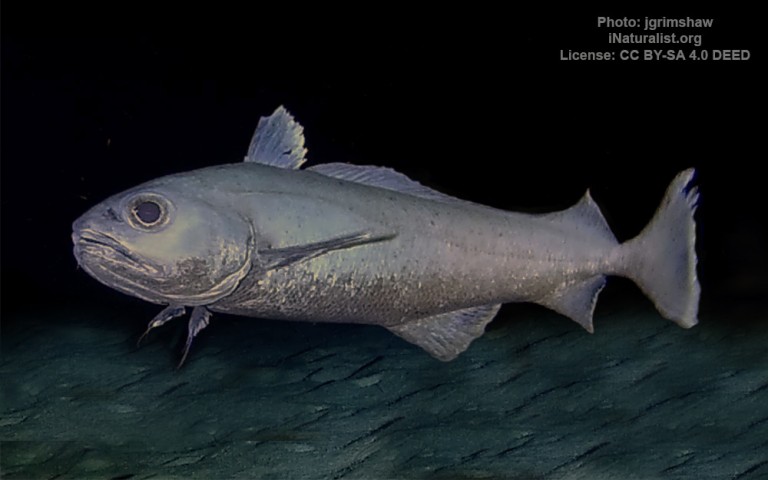
Gadiformes - Cods
Mulliformes - Goatfishes
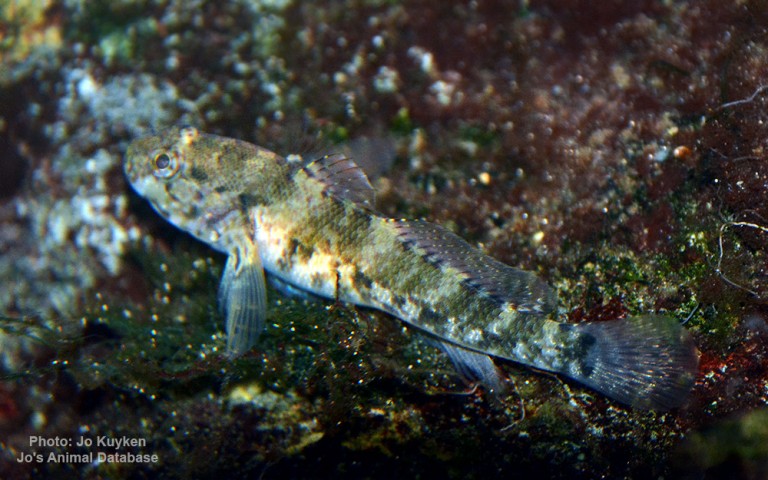
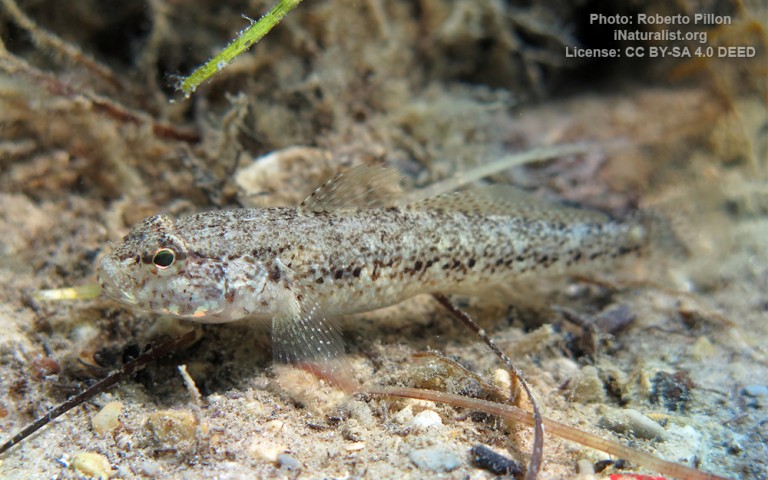
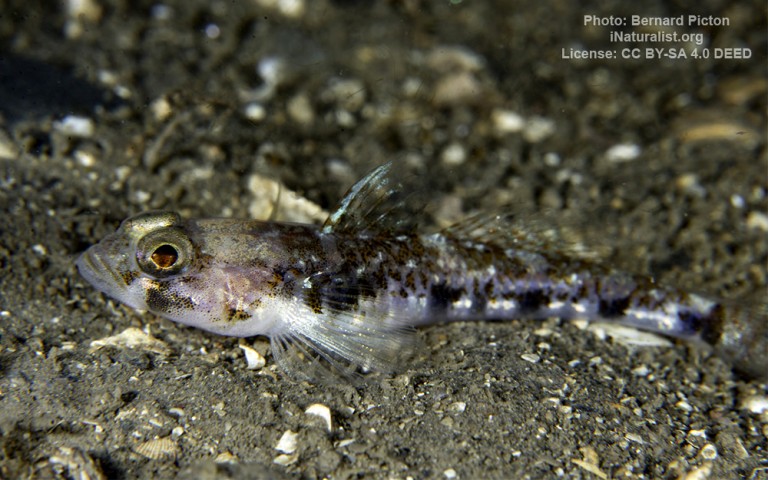
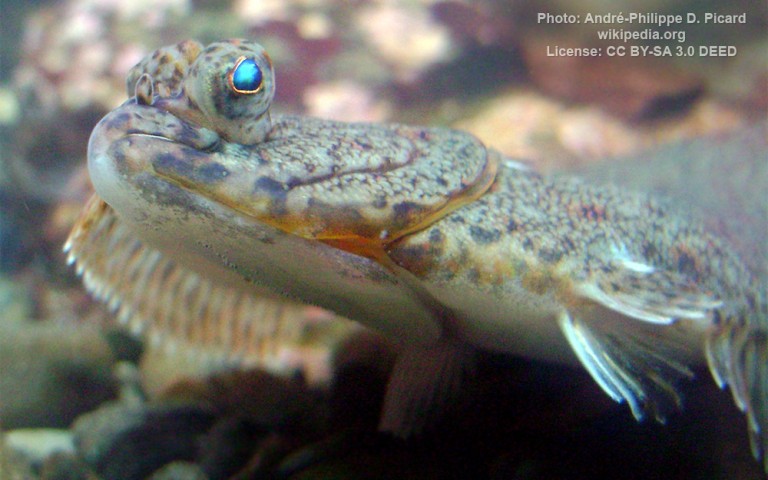
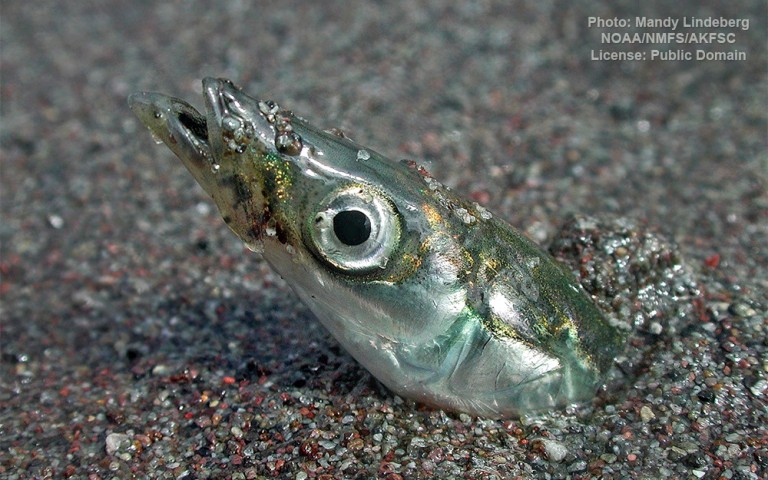
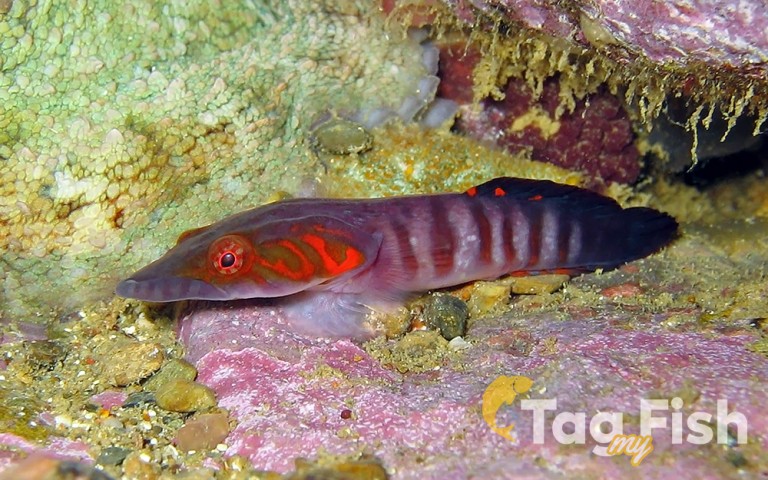
Gobiiformes - Gobies
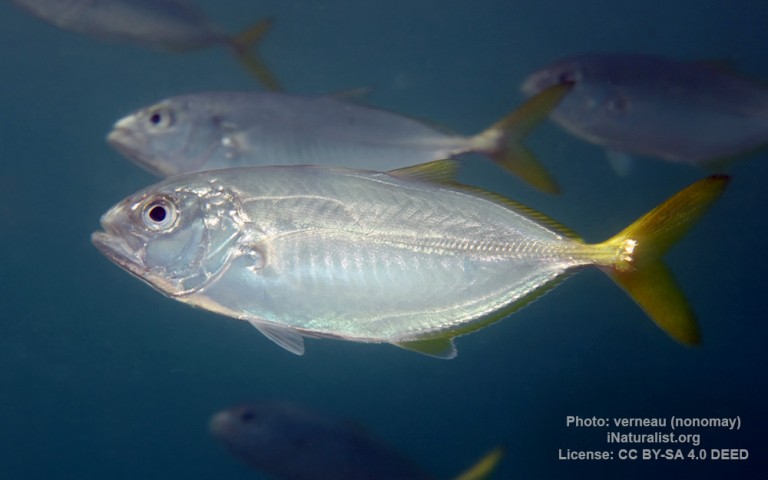
Carangiformes - Jacks
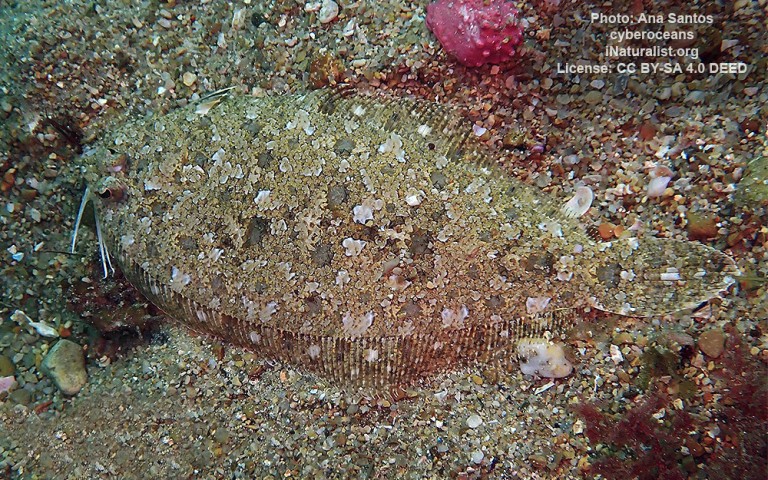
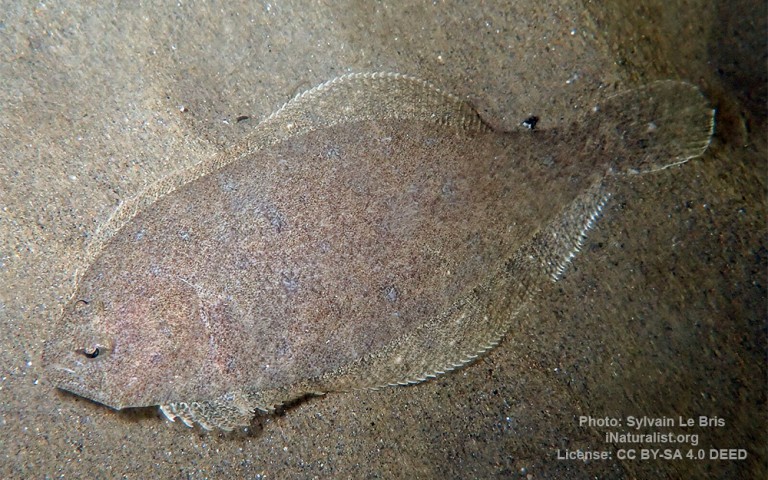
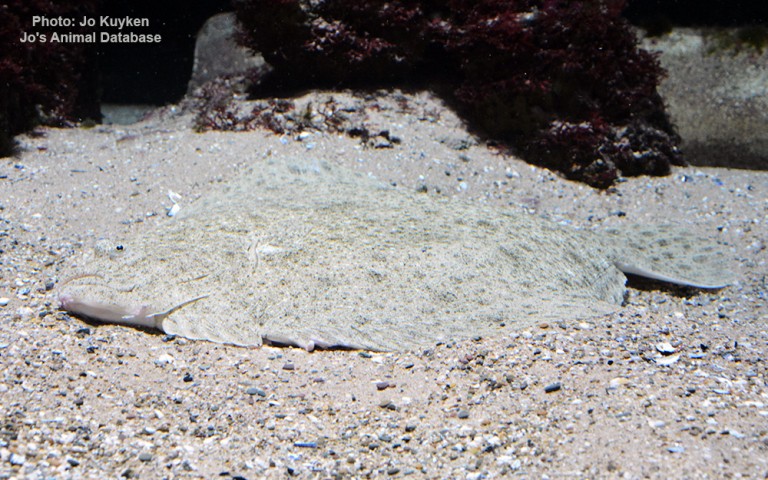
Pleuronectiformes - Flatfishes
Trachiniformes - Weeverfishes
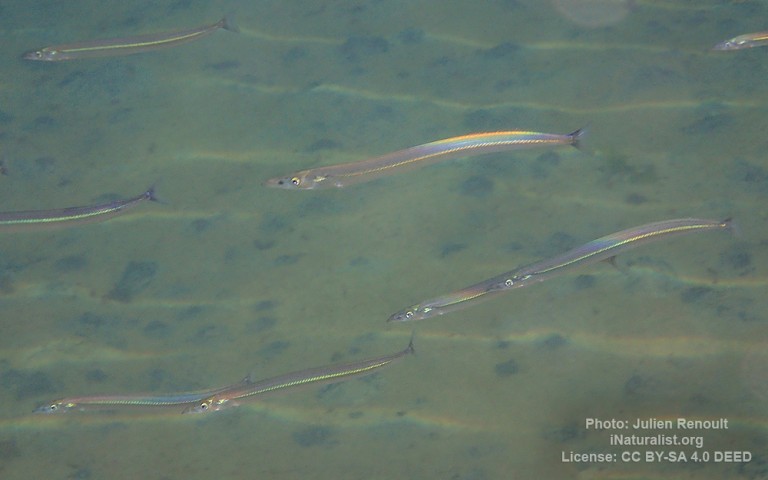
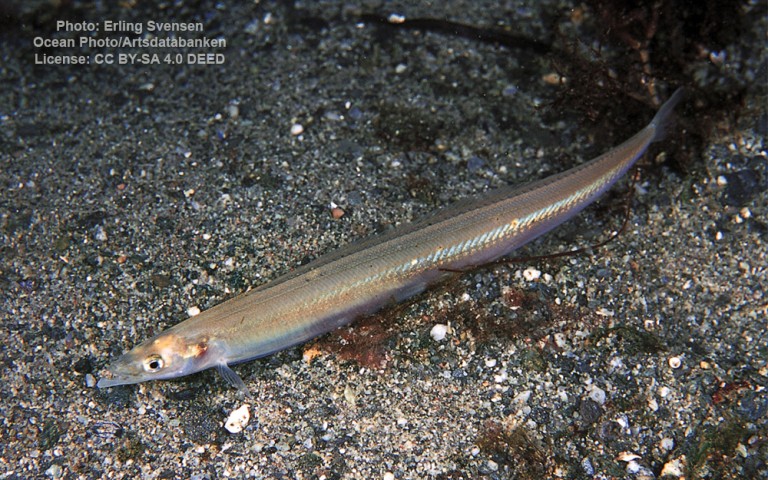
Aulopiformes - Grinners
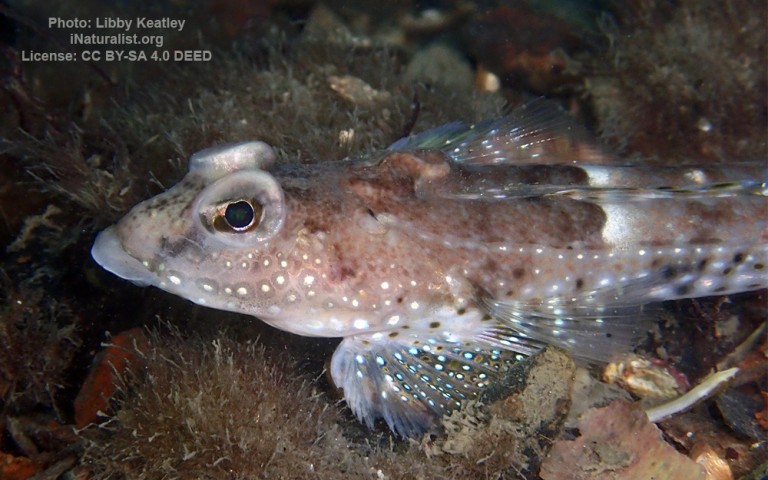
Blenniiformes - Blennies
Lamniformes - Mackerel sharks
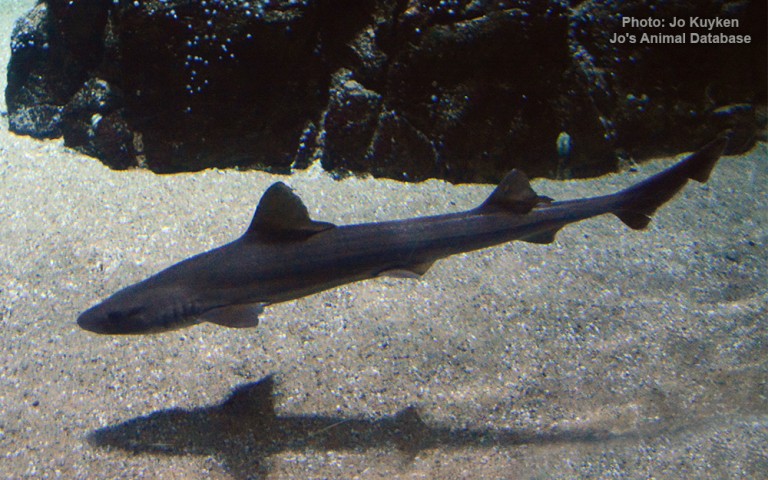
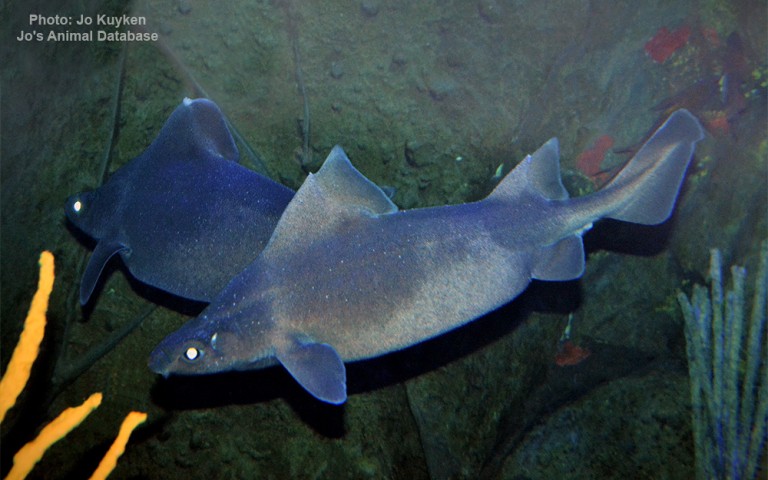
Carcharhiniformes - Ground sharks
Torpediniformes - Electric rays
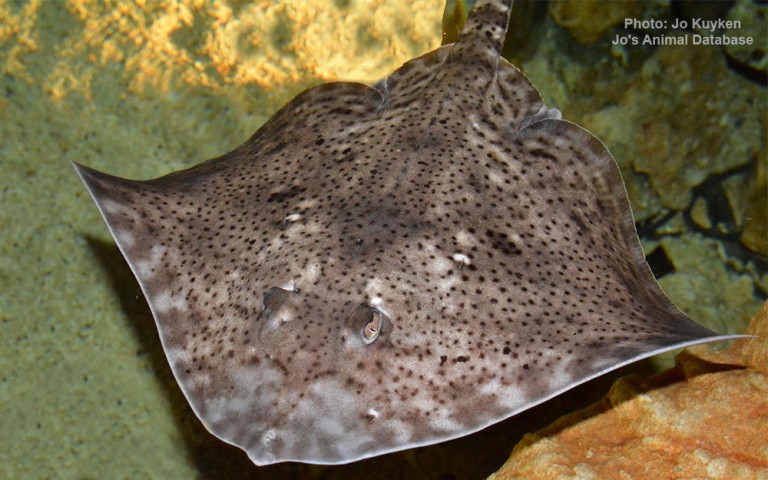
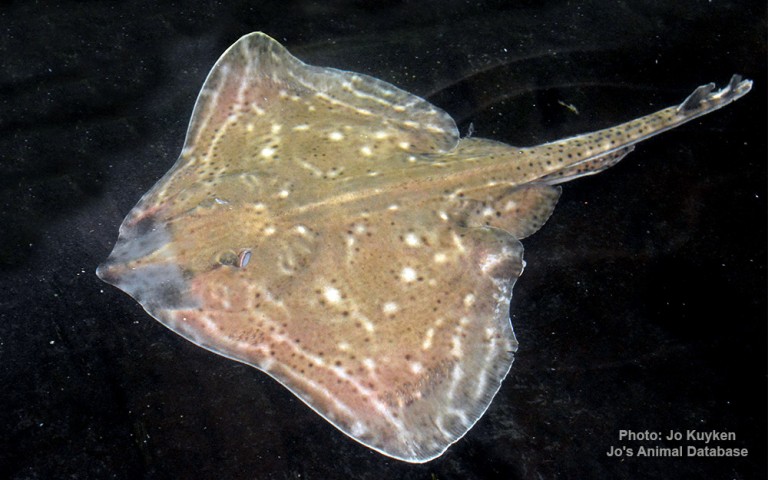
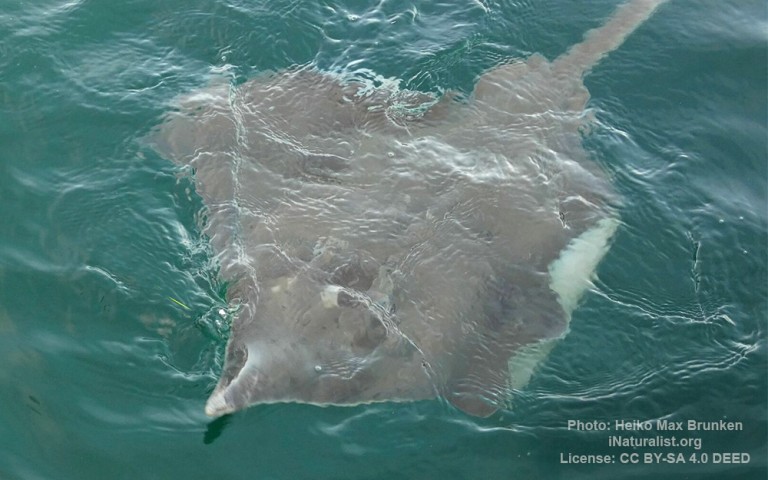
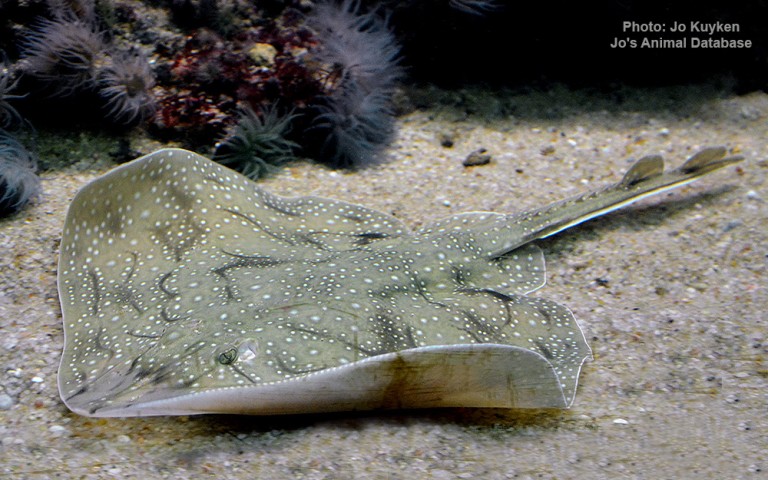
Rajiformes - Skates and rays
Orectolobiformes - Carpet shark
Osmeriformes - Smelts
Chimaeriformes - Chimaeras
Squatiniformes - Angelsharks
Hexanchiformes - Six-gill sharks
Rhinopristiformes - Shovelnose rays
Myxiniformes - Hagfishes
Myliobatiformes - Stingrays
Zeiformes - Dories
Tetraodontiformes - Puffers and filefishes
Dactylopteriformes - Flying gurnards
Lampriformes - Lamprids
Squaliformes - Sleeper and dogfish sharks
Lophiiformes - Anglerfishes
Acanthuriformes - Surgeonfishes
Cyprinodontiformes - Toothcarps
Notacanthiformes - Spiny eels
Saccopharyngiformes - Swallowers and Gulpers
Argentiniformes - Marine smelts
Myctophiformes - Lanternfishes
Beryciformes - Sawbellies
Ophidiiformes - Cusk-eels
Acropomatiformes - Oceanic basses
Atheriniformes - Silversides
Callionymiformes - Dragonets
Gasterosteiformes - Sticklebacks
Gobiesociformes - Clingfishes
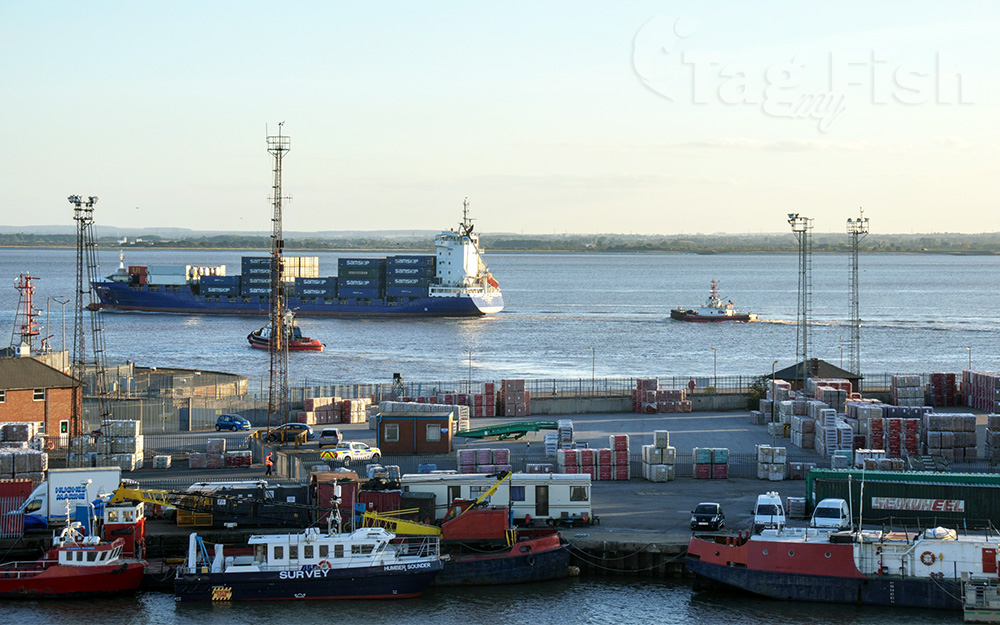
The Humber is a large tidal estuary on the east coast of Northern England. It is formed at Trent Falls, Faxfleet, by the confluence of the tidal rivers Ouse and Trent. From there to the North Sea, it forms part of the boundary between the East Riding of Yorkshire on the north bank and North Lincolnshire on the south bank. Although the Humber is an estuary from the point at which it is formed, many maps show it as the River Humber.
Below Trent Falls, the Humber passes the junction with the Market Weighton Canal on the north shore, the confluence of the River Ancholme on the south shore; between North Ferriby and South Ferriby and under the Humber Bridge; between Barton-upon-Humber on the south bank and Kingston upon Hull on the north bank (where the River Hull joins), then meets the North Sea between Cleethorpes on the Lincolnshire side and the long and thin headland of Spurn Head to the north.
Ports on the Humber include the Port of Hull, the Port of Grimsby and the Port of Immingham; there are lesser ports at New Holland and North Killingholme Haven. The estuary is navigable for the largest of deep-sea vessels. Inland connections for smaller craft are extensive but handle only a quarter of the goods traffic handled in the Thames.
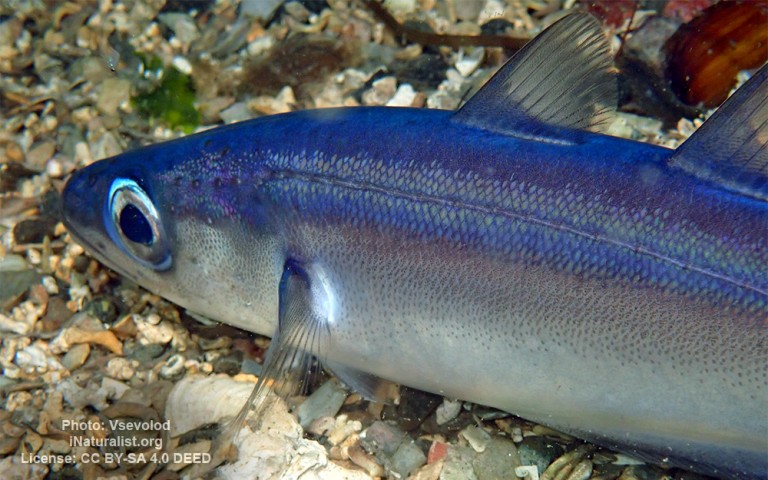
Many fish live in and also migrate along the Humber when returning from the sea to their spawning grounds in Yorkshire, Lincolnshire and Derbyshire. Salmon, sole, cod, eel, flounder, plaice, sprat, lamprey and sand goby have all been caught within the estuary. The Humber is also a good place for over-wintering birds and is a good breeding ground for bitterns, marsh harriers, little terns and avocets. It forms part of the Severn-Trent flyway, a route used by migratory birds to cross Great Britain.
In 2019 the Yorkshire Wildlife Trust and the University of Hull re-introduced the river oyster into the Humber after a sixty-year absence.