Lake Tanganyika

Largest tributaries
Perciformes - Perches
Siluriformes - Catfishes
Cichliformes - Cichlids
Osteoglossiformes - Bony tongues
Characiformes - Characins
Perciformes - Perches
Siluriformes - Catfishes
Cichliformes - Cichlids
Osteoglossiformes - Bony tongues
Characiformes - Characins
Cypriniformes - Carps
Polypteriformes - Bichirs
Ceratodontiformes - Lungfishes
Perciformes - Perches
Siluriformes - Catfishes
Cichliformes - Cichlids
Osteoglossiformes - Bony tongues
Characiformes - Characins
Cypriniformes - Carps
Polypteriformes - Bichirs
Ceratodontiformes - Lungfishes
Lake Tanganyika is an African Great Lake. It is the second-oldest freshwater lake in the world, the second-largest by volume, and the second-deepest, in all cases after Lake Baikal in Siberia. It is the world’s longest freshwater lake.
The lake is shared between four countries—Tanzania, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Burundi, and Zambia, with Tanzania (46%) and DRC (40%) possessing the majority of the lake.
It drains into the Congo River system and ultimately into the Atlantic Ocean.
Lake Tanganyika is situated within the Albertine Rift, the western branch of the East African Rift, and is confined by the mountainous walls of the valley. It is the largest rift lake in Africa and the second-largest lake by volume in the world. It is the deepest lake in Africa and holds the greatest volume of fresh water, accounting for 16% of the world’s available fresh water.
It extends for 676 km (420 mi) in a general north–south direction and averages 50 km (31 mi) in width. The lake covers 32,900 km2 (12,700 sq mi), with a shoreline of 1,828 km (1,136 mi), a mean depth of 570 m (1,870 ft) and a maximum depth of 1,471 m (4,826 ft) (in the northern basin). It holds an estimated 18,900 km3 (4,500 cu mi).
The catchment area of the lake is 231,000 km2 (89,000 sq mi). Two main rivers flow into the lake, as well as numerous smaller rivers and streams (whose lengths are limited by the steep mountains around the lake).
The one major outflow is the Lukuga River, which empties into the Congo River drainage. Precipitation and evaporation play a greater role than the rivers. At least 90% of the water influx is from rain falling on the lake’s surface and at least 90% of the water loss is from direct evaporation.
The major river flowing into the lake is the Ruzizi River, formed about 10,000 years ago, which enters the north of the lake from Lake Kivu.[The Malagarasi River, which is Tanzania’s second largest river, enters the east side of Lake Tanganyika. The Malagarasi is older than Lake Tanganyika, and before the lake was formed, it probably was a headwater of the Lualaba River, the main Congo River headstream.
The lake has a complex history of changing flow patterns, due to its high altitude, great depth, slow rate of refill, and mountainous location in a turbulently volcanic area that has undergone climate changes. Apparently, it has rarely in the past had an outflow to the sea. It has been described as ’practically endorheic’ for this reason. The lake’s connection to the sea is dependent on a high water level allowing water to overflow out of the lake through the Lukuga River into the Congo. When not overflowing, the lake’s exit into the Lukuga River typically is blocked by sand bars and masses of weed, and instead this river depends on its own tributaries, especially the Niemba River, to maintain a flow.
Due to the lake’s tropical location, it has a high rate of evaporation. Thus, it depends on a high inflow through the Ruzizi out of Lake Kivu to keep the lake high enough to overflow. This outflow is apparently not more than 12,000 years old, and resulted from lava flows blocking and diverting the Kivu basin’s previous outflow into Lake Edward and then the Nile system, and diverting it to Lake Tanganyika. Signs of ancient shorelines indicate that at times, Tanganyika may have been up to 300 m (980 ft) lower than its present surface level, with no outlet to the sea. Even its current outlet is intermittent, thus may not have been operating when first visited by Western explorers in 1858.
The lake may also have at times had different inflows and outflows; inward flows from a higher Lake Rukwa, access to Lake Malawi and an exit route to the Nile have all been proposed to have existed at some point in the lake’s history.
Lake Tanganyika is an ancient lake. Its three basins, which in periods with much lower water levels were separate lakes, are of different ages. The central began to form 9–12 million years ago (Mya), the northern 7–8 Mya and the southern 2–4 Mya.
Cichlid fishes
A biologist collecting samples in 2020 in the murky waters of Lake Tanganyika for a study on the diet adaptations of cichlid fishes to better understand their evolution and speciation.
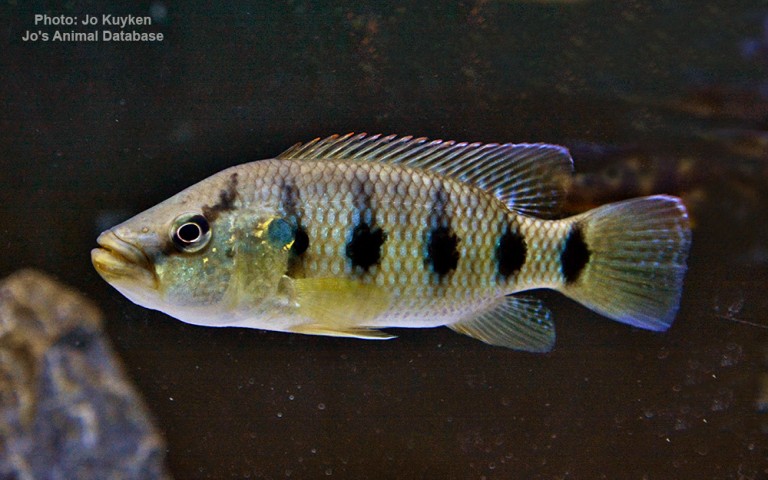
The lake holds at least 250 species of cichlid fish and undescribed species remain. Almost all (98%) of the Tanganyika cichlids are endemic to the lake and it is thus an important biological resource for the study of speciation in evolution. Some of the endemics do occur slightly into the upper Lukuga River, Lake Tanganyika’outflow, but further spread into the Congo River basin is prevented by physics (Lukuga has fast-flowing sections with many rapids and waterfalls) and chemistry (Tanganyika’s water is alkaline, while the Congo’s generally is acidic). The cichlids of the African Great Lakes, including Tanganyika, represent the most diverse extent of adaptive radiation in vertebrates.
Although Tanganyika has far fewer cichlid species than Lakes Malawi and Victoria which both have experienced relatively recent explosive species radiations (resulting in many closely related species), its cichlids are the most morphologically and genetically diverse. This is linked to the high age of Tanganyika, as it is far older than the other lakes.
Tanganyika has the largest number of endemic cichlid genera of all African lakes. All Tanganyika cichlids are in the subfamily Pseudocrenilabrinae. Of the 10 tribes in this subfamily, half are largely or entirely restricted to the lake (Cyprichromini, Ectodini, Lamprologini, Limnochromini and Tropheini) and another three have species in the lake (Haplochromini, Tilapiini and Tylochromini). Others have proposed splitting the Tanganyika cichlids into as many as 12–16 tribes (in addition to previous mentioned, Bathybatini, Benthochromini, Boulengerochromini, Cyphotilapiini, Eretmodini, Greenwoodochromini, Perissodini and Trematocarini).
Most Tanganyika cichlids live along the shoreline down to a depth of 100 m (330 ft), but some deep-water species regularly descend to 200 m (660 ft). Trematocara species have exceptionally been found at more than 300 m (980 ft), which is deeper than any other cichlid in the world. Some of the deep-water cichlids (e.g., Bathybates, Gnathochromis, Hemibates and Xenochromis) have been caught in places virtually devoid of oxygen, but how they are able to survive there is unclear.
Tanganyika cichlids are generally benthic (found at or near the bottom) and/or coastal. No Tanganyika cichlids are truly pelagic and offshore, except for some of the piscivorous Bathybates. Two of these, B. fasciatus and B. leo, mainly feed on Tanganyika sardines. Tanganyika cichlids differ extensively in ecology and include species that are herbivores, detritivores, planktivores, insectivores, molluscivores, scavengers, scale-eaters and piscivores. These dietary specializations, however, have been shown to be flexible. That is, many species of Tanganyikan cichlid with specialized diets showed opportunistic, episodic exploitation of Stolothrissa tanganicae and Limnothrissa miodon when prey concentrations were unusually high.
Their breeding behavior fall into two main groups, the substrate spawners (often in caves or rock crevices) and the mouthbrooders. Among the endemic species are two of the world’s smallest cichlids, Neolamprologus multifasciatus and N. similis (both shell dwellers) at up to 4–5 cm (1.6–2.0 in), and one of the largest, the giant cichlid (Boulengerochromis microlepis) at up to 90 cm (3.0 ft).
Many cichlids from Lake Tanganyika, such as species from the genera Altolamprologus, Cyprichromis, Eretmodus, Julidochromis, Lamprologus, Neolamprologus, Tropheus and Xenotilapia, are popular aquarium fish due to their bright colors and patterns, and interesting behaviors. Recreating a Lake Tanganyika biotope to host those cichlids in a habitat similar to their natural environment is also popular in the aquarium hobby.
Other fishes
Lake Tanganyika is home to more than 80 species of non-cichlid fish and about 60% of these are endemic.
The open waters of the pelagic zone are dominated by four non-cichlid species: Two species of Tanganyika sardine (Limnothrissa miodon and Stolothrissa tanganicae) form the largest biomass of fish in this zone, and they are important prey for the forktail lates (Lates microlepis) and sleek lates (L. stappersii). Two additional lates are found in the lake, the Tanganyika lates (L. angustifrons) and bigeye lates (L. mariae), but both these are primarily benthic hunters, although they also may move into open waters. The four lates, all endemic to Tanganyika, have been overfished and larger individuals are rare today.
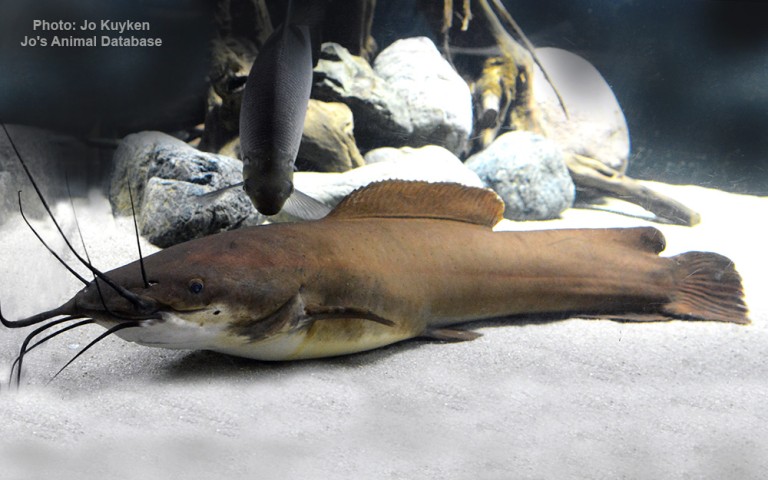
Among the more unusual fish in the lake are the endemic, facultatively brood parasitic cuckoo catfish, including at least Synodontis grandiops and S. multipunctatus. A number of others are very similar (e.g., S. lucipinnis and S. petricola) and have often been confused; it is unclear if they have a similar behavior. The facultative brood parasites often lay their eggs synchronously with mouthbroding cichlids. The cichlid pick up the eggs in their mouth as if they were their own. Once the catfish eggs hatch the young eat the cichlid eggs.
Six catfish genera are entirely restricted to the lake basin: Bathybagrus, Dinotopterus, Lophiobagrus, Phyllonemus, Pseudotanganikallabes and Tanganikallabes. Although not endemic on a genus level, six species of Chrysichthys catfish are only found in the Tanganyika basin where they live both in shallow and relatively deep waters; in the latter habitat they are the primary predators and scavengers. A unique evolutionary radiation in the lake is the 15 species of Mastacembelus spiny eels, all but one endemic to its basin.
Although other African Great Lakes have Synodontis catfish, endemic catfish genera and Mastacembelus spiny eels, the relatively high diversity is unique to Tanganyika, which likely is related to its old age.
Among the non-endemic fish, some are widespread African species but several are only shared with the Malagarasi and Congo River basins, such as the Congo bichir (Polypterus congicus), goliath tigerfish (Hydrocynus goliath), Citharinus citharus, six-banded distichodus (Distichodus sexfasciatus) and mbu puffer (Tetraodon mbu).