Timor sea

Water type: Sea
Connection to the ocean: Indian ocean
Continents:
Asia, Australia & Oceania
Climate:
Tropical
Bays
Largest tributaries
Mugiliformes - Mullets
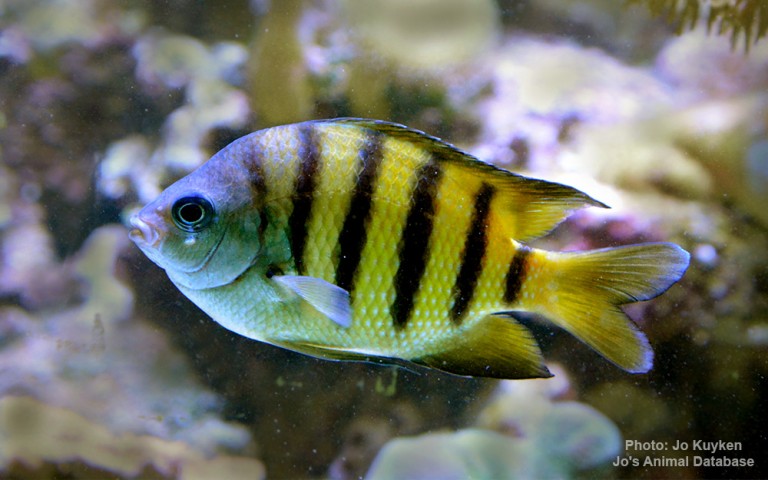
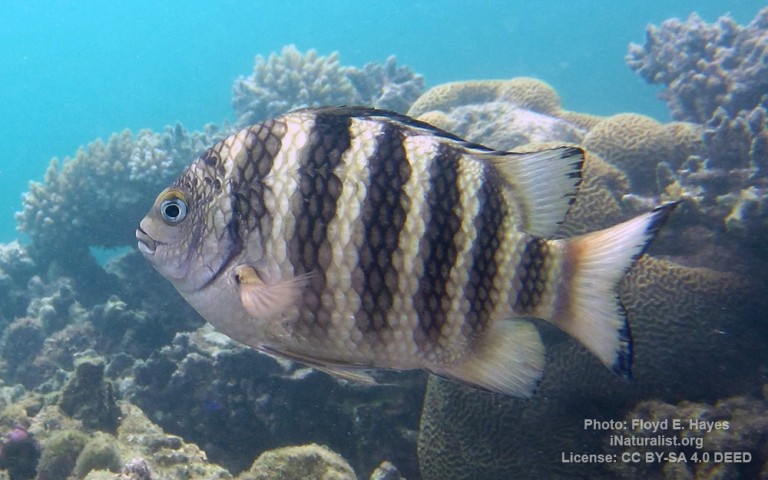
Perciformes - Perches
Carangiformes - Jacks
Istiophoriformes - Barracudas
Scorpaeniformes - Mail-cheeked fishes
Lamniformes - Mackerel sharks
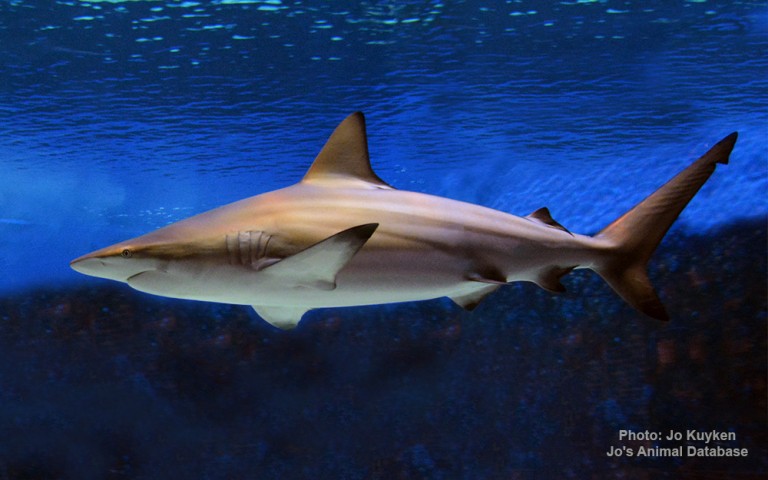
Carcharhiniformes - Ground sharks
Orectolobiformes - Carpet shark
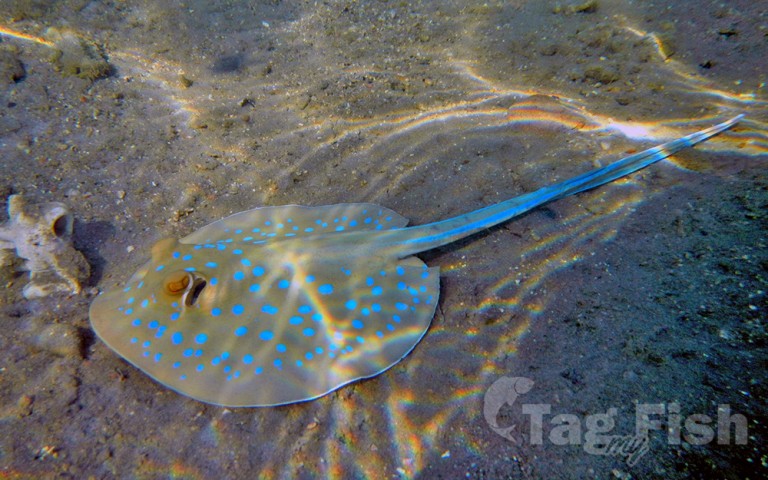
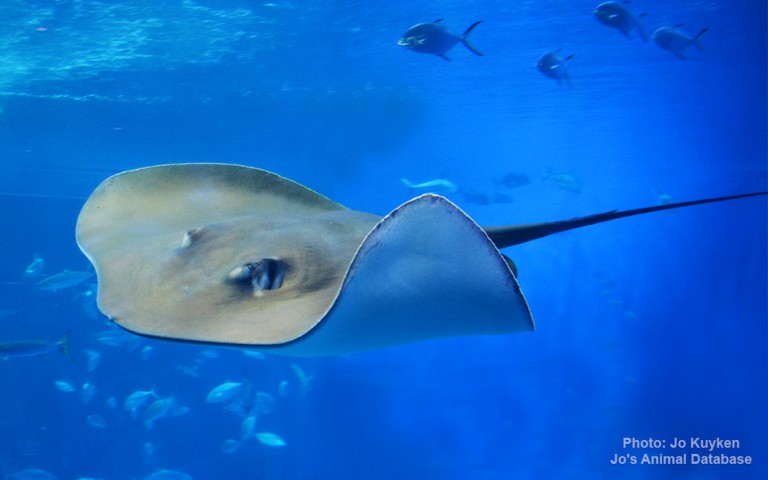
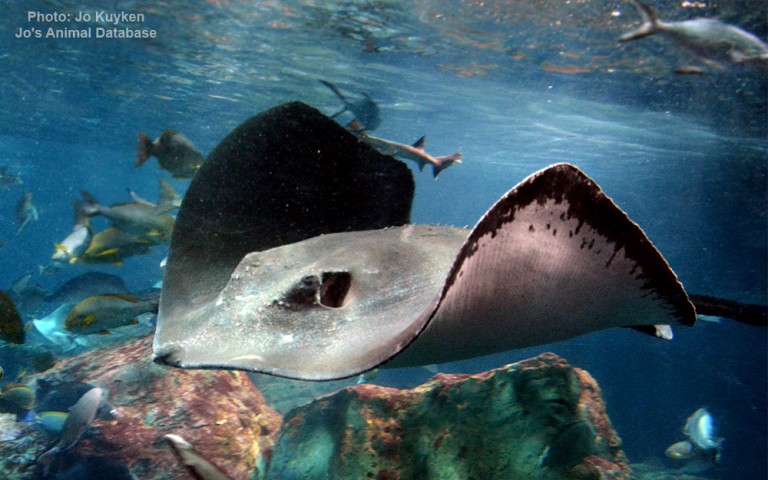
Myliobatiformes - Stingrays
Scombriformes - Mackerels
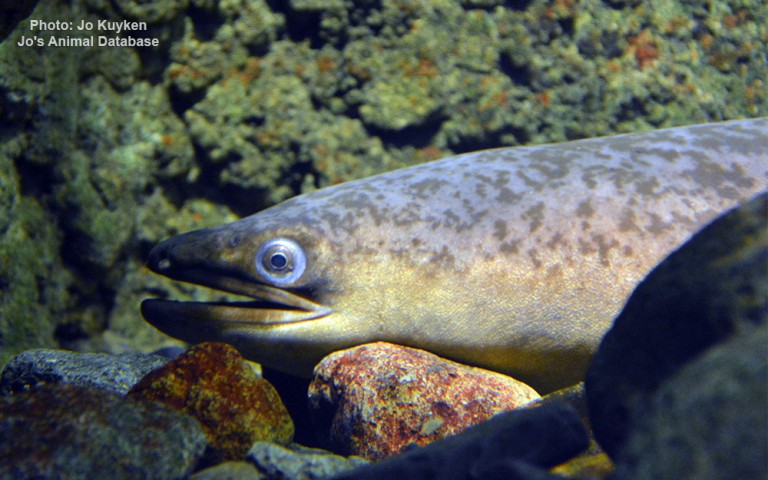
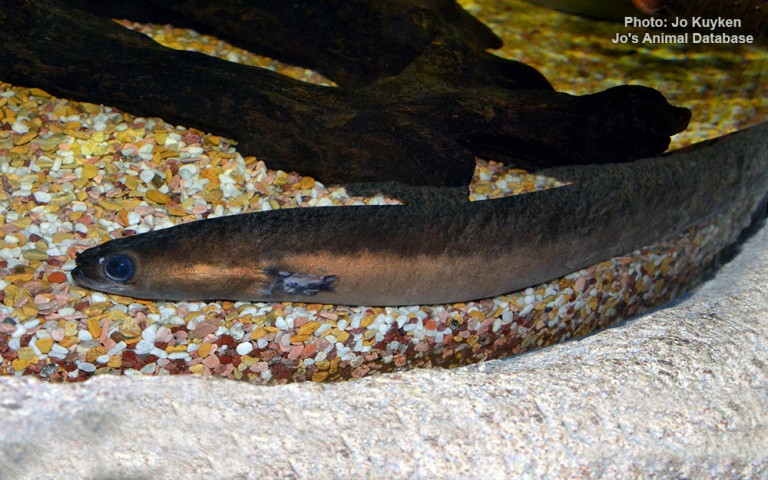
Anguilliformes - Eels and morays
Tetraodontiformes - Puffers and filefishes
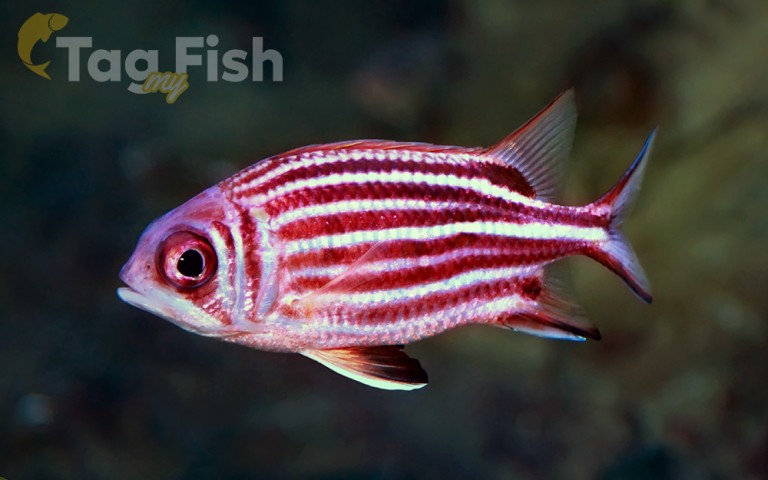
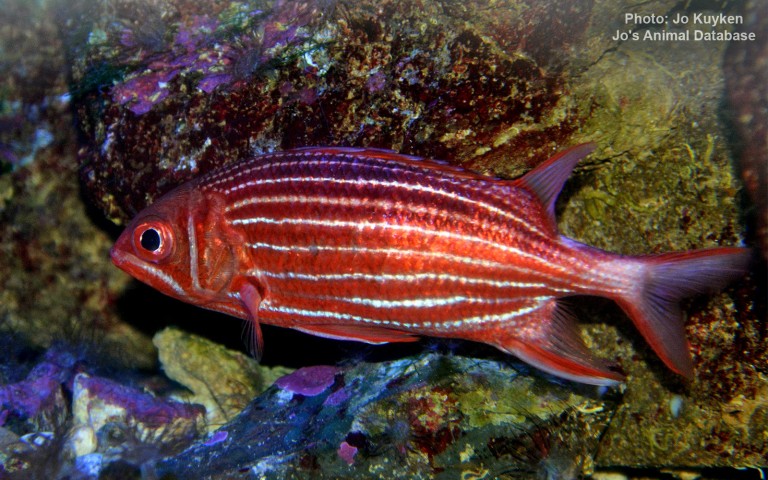
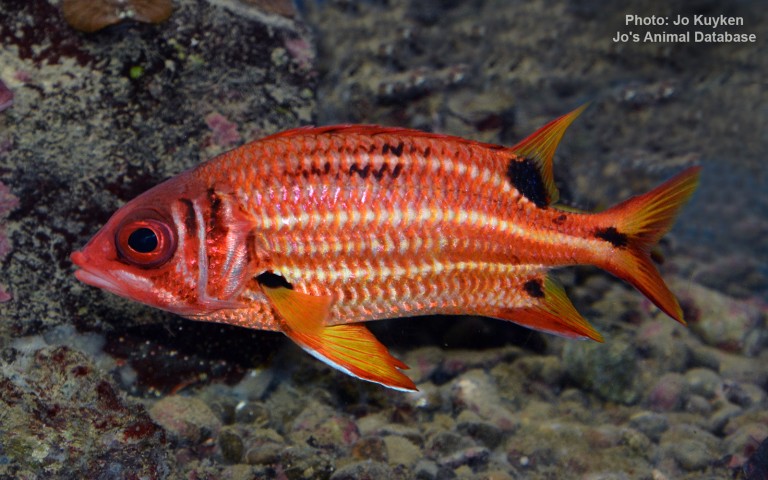
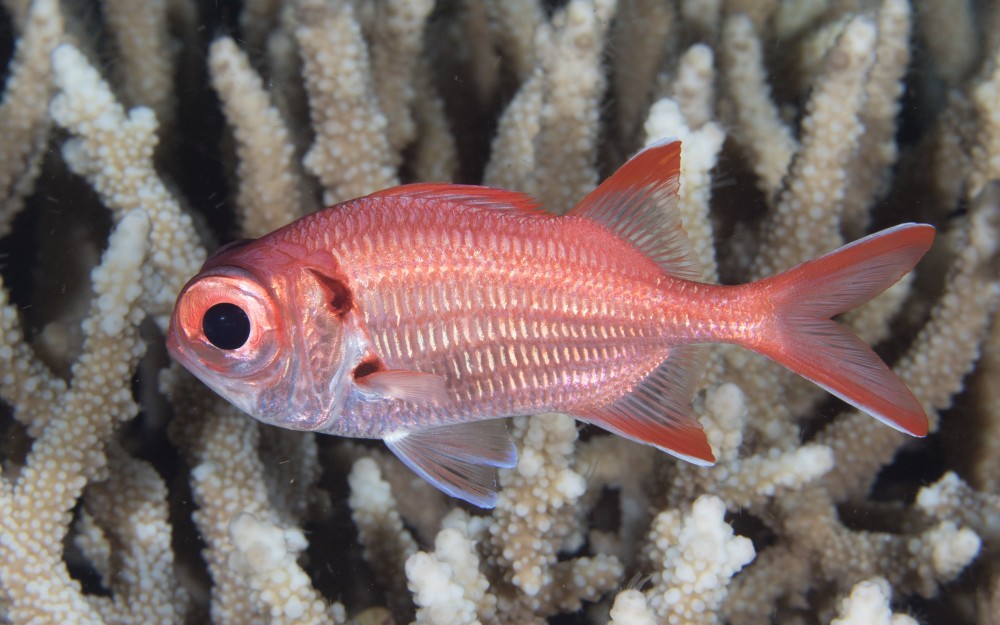
Holocentriformes - Squirrelfishes
Lophiiformes - Anglerfishes
Acanthuriformes - Surgeonfishes
Labriformes - Wrasses
Gobiiformes - Gobies
Lampriformes - Lamprids
Mulliformes - Goatfishes
Gadiformes - Cods
Spariformes - Breams and porgies
Syngnathiformes - Pipefishes and Seahorses
Gonorynchiformes - Milkfishes
Beryciformes - Sawbellies
Ophidiiformes - Cusk-eels
Acropomatiformes - Oceanic basses
Centrarchiformes - Basses and sunfishes
Beloniformes - Needlefishes
Trachiniformes - Weeverfishes
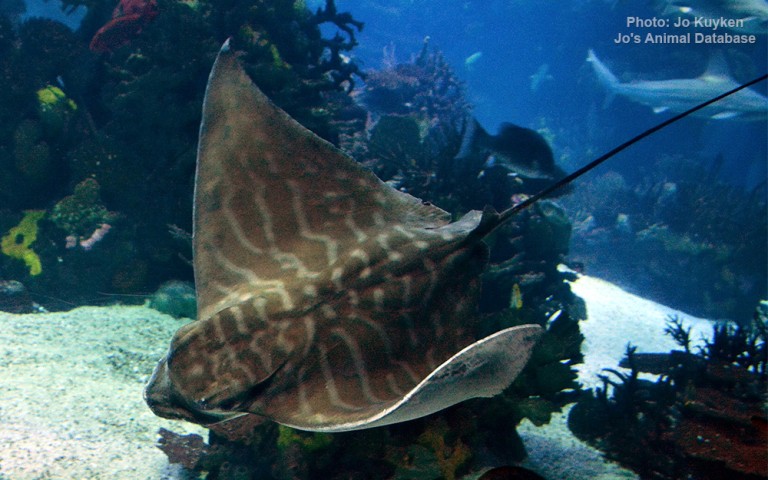
Rhinopristiformes - Shovelnose rays
Kurtiformes - Nurseryfishes & Cardinalfishes
Pleuronectiformes - Flatfishes
Aulopiformes - Grinners
Blenniiformes - Blennies
Atheriniformes - Silversides
Albuliformes - Bonefishes
Siluriformes - Catfishes
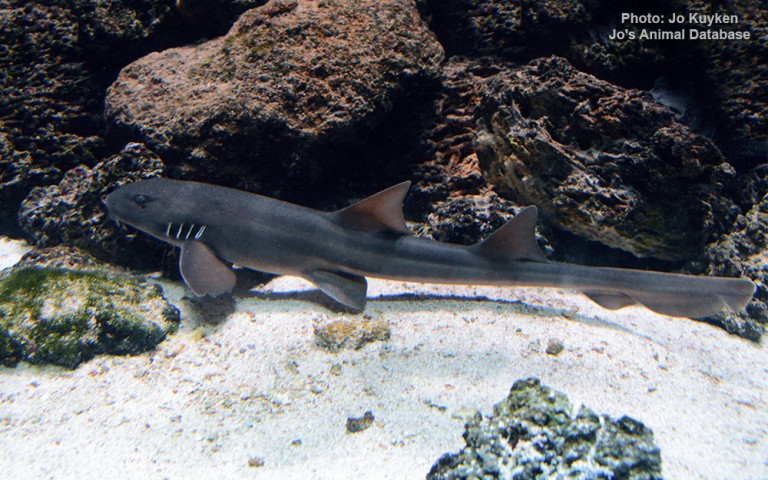
Heterodontiformes - Bullhead and horn sharks
The Timor Sea is a relatively shallow sea bounded to the north by the island of Timor (Asian continent), to the east by the Arafura Sea, and to the south by Australia.
The sea contains a number of reefs, uninhabited islands and significant hydrocarbon reserves. International disputes emerged after the reserves were discovered resulting in the signing of the Timor Sea Treaty.
The Timor Sea was hit by the worst oil spill for 25 years in 2009.